1. Recycling Technology for Disposable Diaper Waste
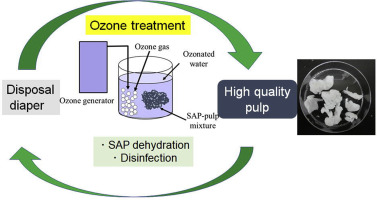
As Japan’s population continues to age, the volume of used disposable diapers is rapidly increasing. Currently, most of these products are disposed of through incineration. However, the high moisture content of used diapers necessitates significant amounts of auxiliary fuel, leading to increased operational costs and higher volumes of incineration residue. Furthermore, the intense heat generated during the process can accelerate the thermal degradation of incinerators, shortening their lifespan and increasing maintenance expenses. In response to these challenges, the Ministry of the Environment has issued guidelines to promote the recycling of disposable diapers.
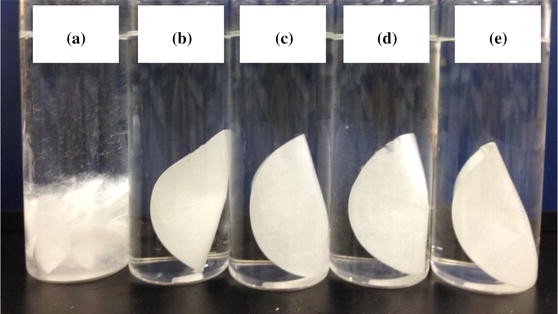
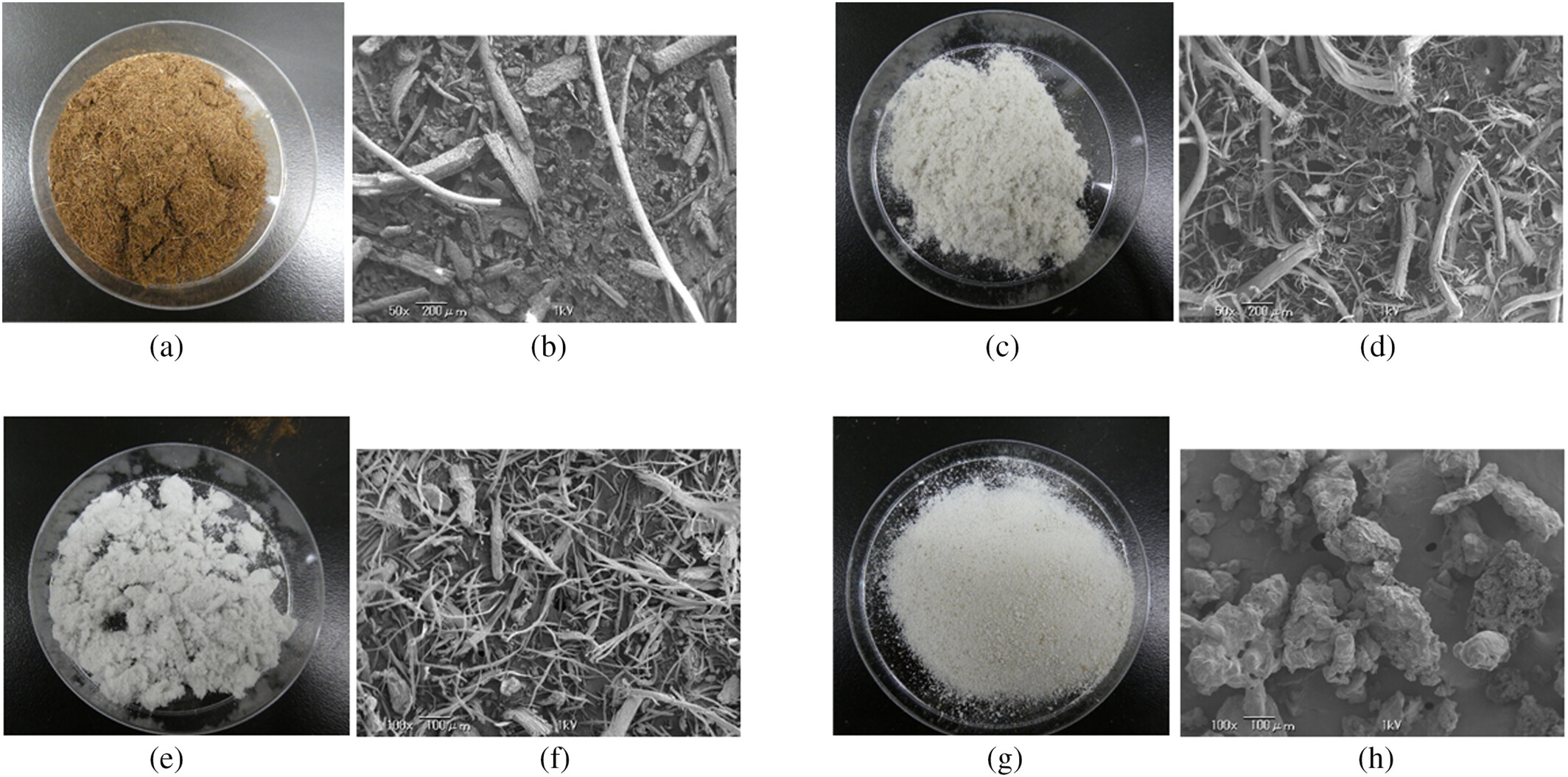
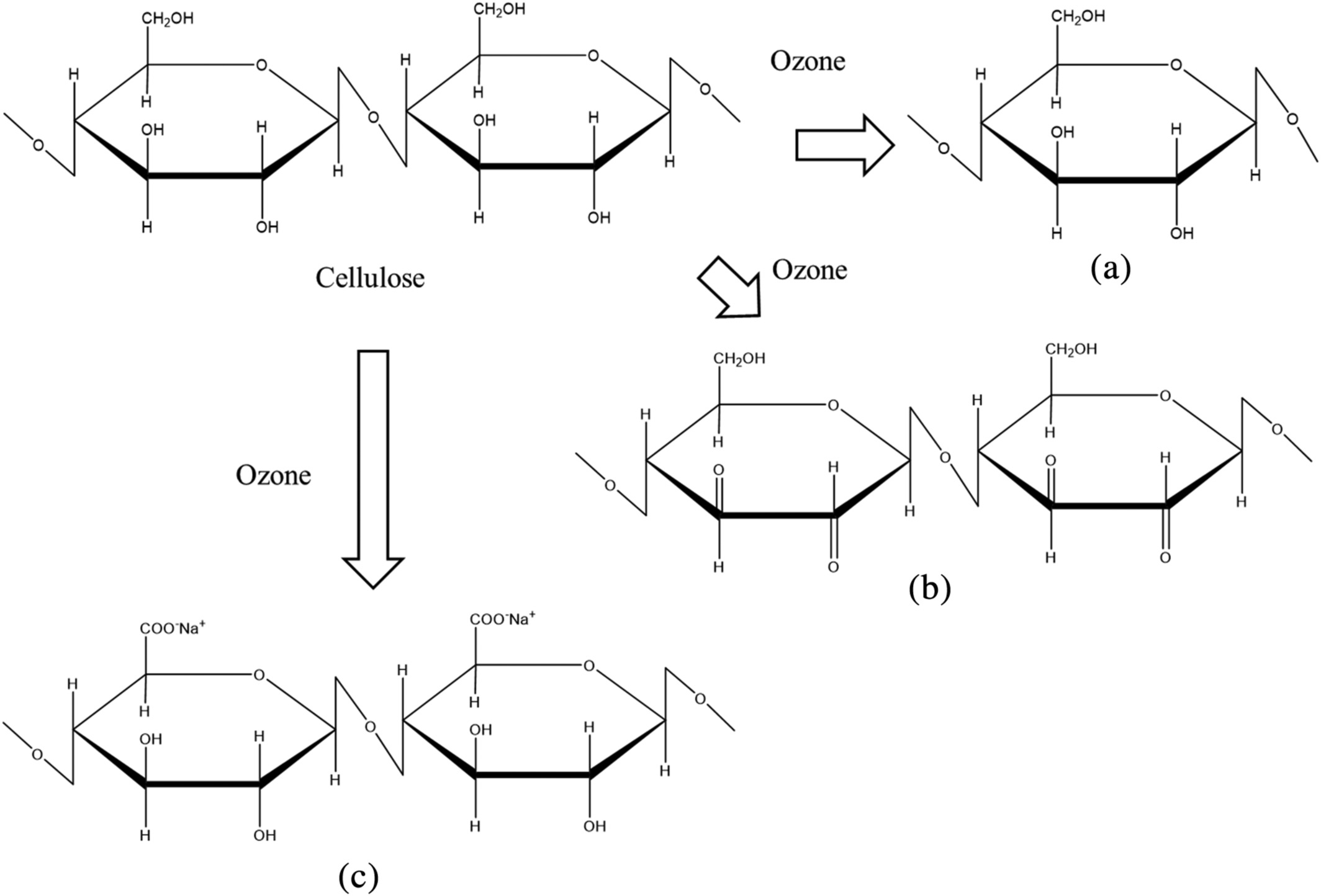
To address this need, our laboratory has developed a novel ozone-based recycling technology. This innovation allows for the efficient recovery of high-quality pulp from used diapers—a feat previously considered technically difficult. This recovered pulp can now be reintegrated into the production cycle for new disposable diapers.
A demonstration test of this technology is currently underway in Shibushi City, Kagoshima Prefecture. Building on this success, full-scale implementation is scheduled to commence in fiscal 2023, marking the launch of a landmark project to manufacture disposable diapers using recycled pulp.
Related paper
・Journal of cleaner production 276, 123350 (2020), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123350.
2. Development of Biodegradable Materials Using Cellulose
This research focuses on developing high-performance biodegradable materials derived from wood-based cellulose. As the global demand for sustainable alternatives to synthetic plastics grows, paper-based materials have gained significant attention. However, traditional paper faces two major technical hurdles: insufficient wet tensile strength and the difficulty of controlling biodegradation rates. For instance, in agricultural applications such as mulch films, premature decomposition before crop maturation renders the film ineffective.
To address these challenges, our laboratory is investigating a straightforward yet effective chemical treatment using phosphoric acid and urea. This method enhances the wet strength of cellulose-based sheets while simultaneously providing precise control over microbial degradation. By optimizing these properties, we aim to develop durable, functional paper materials that contribute to a more sustainable bio-economy.
Related paper
・ Cellulose, 26, 5105-5116 (2019) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02423-y
-
Challenges of Paper Mulch
-
Phosphate-Urea Treatment
-
Improvement in wet paper strength
-
Biodegradability Test
3. Development of Functional Paper Using Ionic Liquids
Our laboratory investigates the enhancement of paper properties by utilizing ionic liquids—a unique class of solvents capable of dissolving cellulose. Traditionally, polyamide-polyamine-epichlorohydrin (PAE) resins have been widely used as wet-strength agents for products such as water-resistant corrugated board, paper towels, and tissues. However, due to the toxicity of by-products generated during PAE production, there is an urgent global demand for environmentally friendly alternatives.
In this study, we achieved high wet-strength paper through a controlled partial dissolution and regeneration process using ionic liquids. This method allows for the creation of high-strength materials composed entirely of cellulose, eliminating the need for synthetic resins.
Beyond mechanical strength, paper treated with ionic liquids exhibits significantly improved specific surface area, moisture retention, and adsorption rates (e.g., for polyethylene glycol). By integrating functional additives like activated carbon or catalysts, these materials can be transformed into high-performance water purification filters or catalytic sheets capable of operating effectively in aqueous environments.
Related paper
・Cellulose 27, 8317-8327 (2020), DOI: 10.1007/s10570-020-03303-6.
・Cellulose, 24(8), 3469-3477 (2017). DOI: 10.1007/s10570-017-1340-8.
・Cellulose, 32, 4341-4344 (2025). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-025-06512-z
4. Utilization of Palm Fiber (International Collaboration with Indonesia)
This study is an international collaborative project focused on the sustainable valorization of waste generated by the palm oil industry in Indonesia. As palm oil accounts for approximately 12% of Indonesia's export economy, the industry generates a massive volume of biomass waste, with palm fiber (Empty Fruit Bunches) constituting 22–24% of the total. Given that these fibers contain approximately 50% cellulose, our research aims to transform this abundant waste stream into high-value cellulose derivatives.
In this project, we successfully synthesized Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) from recovered palm fiber for applications in the food industry. By integrating ozone treatment into the process, we were able to precisely tailor the physicochemical properties of the CMC, such as its viscosity and solubility. This advanced processing technique adds significant functional value to the material, turning industrial waste into a premium bio-based ingredient for a circular economy.
Related paper
・Journal of applied polymer science 138, e54228 (2023), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.54228
・Journal of applied polymer science 138, e49610 (2021), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49610
5. Intelligent Functional Paper and Nonwovens
Smart materials are defined by their ability to exhibit specific functions in response to changes in their external environment. We are applying this intelligent material concept to paper and nonwoven fabrics, creating a new class of functional sheets with integrated environmental sensing capabilities.
Our research has successfully developed paper that responds to biological analytes and temperature fluctuations. Furthermore, we have engineered intelligent functionalities that allow for the controlled release of fragrances in response to specific external stimuli. By merging the versatility of fibrous sheets with advanced chemical responsiveness, we aim to produce novel materials for applications in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and smart packaging.
-
Intelligent functional paper
-
Temperature responsiveness
-
Body Component Responsiveness
-
Moisture-responsive
Related paper
・ Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 134(9) , 44530 (2017) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44530.
・Chemical Engineering Journal, 245, 17-23(2014). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.019
・Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 129, 2139-2144 (2013). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.38941
・Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 127, 1725-1729 (2013). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37902.
・ Journal of Materials Science, 45, 1343-1349 (2010) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4088-1.
・Journal of Materials Science, 44, 992-997 (2009).DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3220-y
・Journal of Materials Science, 43, 1486-1491 (2008). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2341-z
・ Journal of Materials Science, 40, 1987-1991 (2005).DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-1221-7
6. Paper Sludge Recycling and Resource Recovery
In the pulp and paper industry, paper sludge management remains a significant environmental challenge. Traditionally, the organic pulp fraction of the sludge is incinerated for energy, while the remaining inorganic fillers are consigned to landfills. Research has primarily focused on reusing the inorganic residues, as the complex mixture of pulp and minerals makes efficient separation technically difficult.
To address this, our laboratory has developed a novel approach to separate and recover these components using ionic liquids. By leveraging the unique ability of ionic liquids to selectively dissolve cellulose, we can isolate the pulp fraction from the inorganic minerals. This process facilitates the high-purity fractionation of both organic and inorganic materials, enabling their independent recovery and high-value upcycling. This technology offers a sustainable pathway toward transforming industrial waste into valuable raw materials.
Related paper
・ Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, SPECIAL FEATURE: ORIGINAL
ARTICLE AGRO' 2014,18(2), 215-221, (2016). DOI :https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-015-0391-x
・ Chemical Engineering Journal, 173, 129-134 (2011) DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.048
7. Functional Paper via Interfacial Polymerization
Our research explores the functionalization of fibrous sheet materials—such as paper and nonwovens—under the core concept of "nano-interface control." Unlike conventional coating methods, we employ in-situ interfacial polymerization to simultaneously synthesize and immobilize functional polymers directly onto the fiber surfaces.
This approach allows us to precisely engineer the morphology of the resulting polymer films, creating structures such as microcapsules, nanofibers, and porous matrices. By elucidating the underlying mechanisms of these morphological transitions, we can tailor the material's properties for specific applications.
Practical applications of this technology include the development of insect-repellent paper with sustained-release capabilities and linerless adhesive paper, which eliminates the need for disposable release liners. Through the integration of interfacial chemistry and paper science, we are creating next-generation sheet materials with unprecedented functionalities.
Related paper
・Ichiura H., Kawahara U., “Polyamide film containing a molecularly imprinted
polymer prepared on a paper surface by interfacial polymerization and its
selective adsorption of benzalkonium chloride”, Journal of applied polymer
science, e55077 (2023). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.55077.
・Chemosphere, 256, 127143 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127143
・ Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 55(4), 961-966 (2016).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04548
・ Polymer bulletin, 72, 2621-2632 (2015). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1426-0
・ Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 9137-9144 (2013).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ie401082a
・Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 124, 242-247 (2012). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.33900
・Journal of Materials Science, 41, 7019-7024 (2006).DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0789-x